C4 Architecture Model
Introduction
The C4 model is a framework for visualizing the architecture of software systems. It provides a hierarchical approach to modeling, allowing you to create diagrams at different levels of abstraction. The C4 model consists of four main diagram types:
- Context Diagram: Shows the system’s context and its interactions with external entities.
- Container Diagram: Breaks down the system into containers (applications or services) and their relationships.
- Component Diagram: Details the internal structure of a container, showing its components and their interactions.
- Code Diagram: Focuses on the code structure within a component, such as classes or modules.
Advantages
- Clarity: Provides a clear and structured way to visualize complex systems.
- Documentation: Serves as living documentation that evolves with the system.
- Scalability: Allows you to zoom in and out of different levels of detail (my favorite).
- Collaboration: Facilitates communication among team members and stakeholders.
- Onboarding: Helps new team members understand the system architecture quickly.
Structure
The C4 model uses a specific structure for its diagrams, which includes:
- Elements: Represent entities such as people, software systems, containers, and components.
- Relationships: Show how elements interact with each other.
- Styles: Define the appearance of elements and relationships in the diagrams.
Docs and tools
The c4 model documentation is available at c4model.com . It provides detailed guidelines on how to create C4 diagrams, including examples and best practices.
To create a c4 model diagram, you can use various tools such as:
- Structurizr: A web-based tool for creating C4 diagrams.
- PlantUML: A text-based tool that supports C4 diagrams.
- Draw.io: A general-purpose diagramming tool that can be used for C4 diagrams.
- …
The following examples uses Structurizr DSL , which is a domain-specific language for defining C4 models. It allows you to create C4 diagrams using a simple text format.
Example code
The following code represents a simple C4 model for a webshop system with a user, a frontend, a backend, and a database. It includes identifiers, models, views, and styles.
(Scroll down to see the generated diagram.)
workspace "Webshop Architecture" "Architecture model for an e-commerce webshop system" {
!identifiers hierarchical
model {
# People
u = person "Customer" "A person who wants to purchase products online"
admin = person "Administrator" "Staff member who manages products and orders"
# Software System
sws = softwareSystem "Webshop System" "E-commerce platform for online shopping" {
# Frontend Container
webShopFrontend = container "Webshop Frontend" "Single-page application providing the user interface" "React, TypeScript" {
productCatalog = component "Product Catalog" "Shows available products with filtering and search" "React Components"
shoppingCart = component "Shopping Cart" "Manages items selected for purchase" "React, Redux"
checkout = component "Checkout Flow" "Handles payment and order completion" "React, Payment API"
userAccount = component "User Account Panel" "Manages user profile and order history" "React Components"
}
# Backend Container
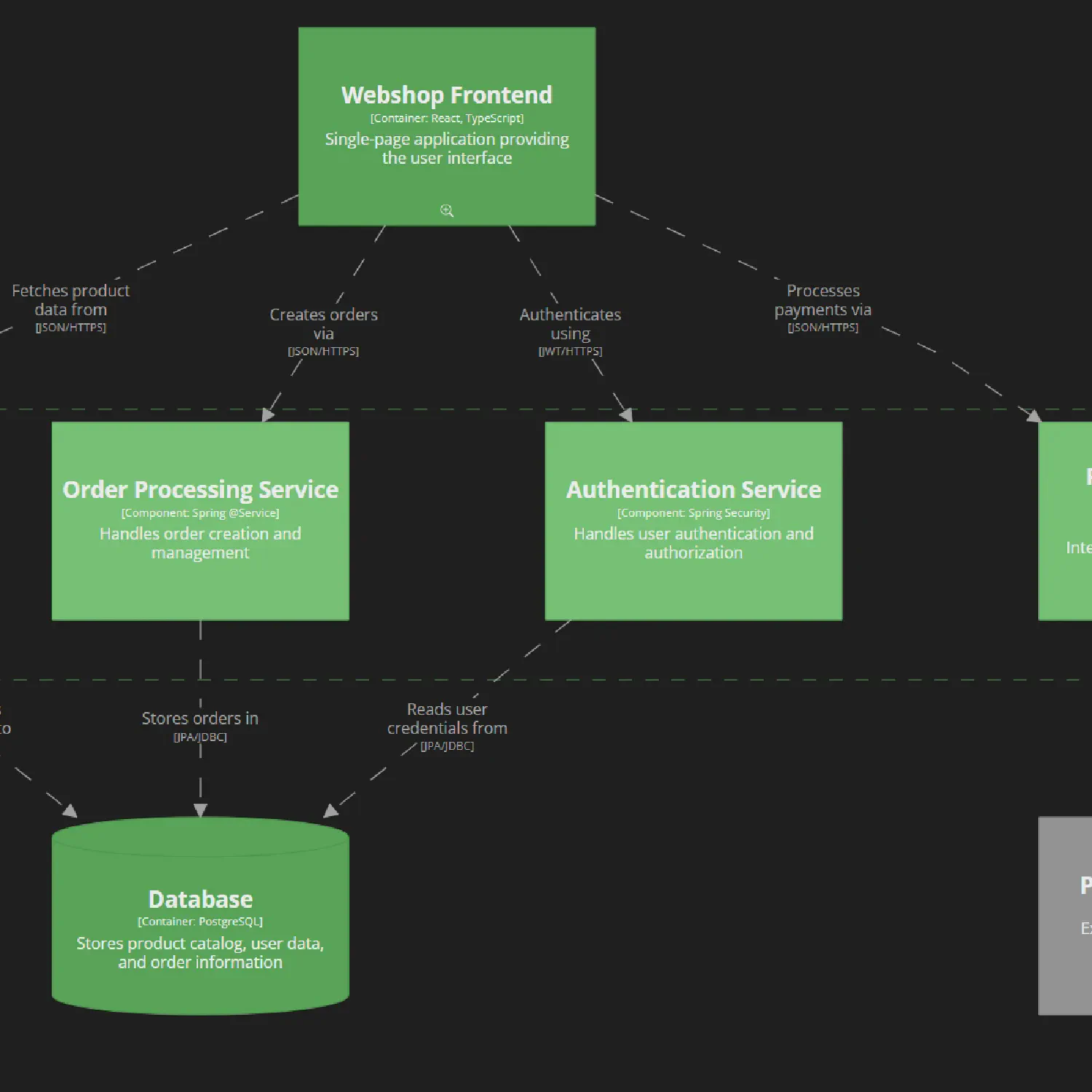
webShopBackend = container "Webshop Backend" "REST API handling business logic and data access" "Spring Boot, Java" {
productService = component "Product Service" "Manages product catalog and inventory" "Spring @RestController"
orderService = component "Order Processing Service" "Handles order creation and management" "Spring @Service"
authService = component "Authentication Service" "Handles user authentication and authorization" "Spring Security"
paymentGateway = component "Payment Gateway Connector" "Interfaces with external payment processors" "Java HTTP Client"
}
# Database Container
db = container "Database" "Stores product catalog, user data, and order information" "PostgreSQL" {
tags "Database"
}
}
# External Systems
paymentSystem = softwareSystem "Payment Processor" "External payment processing service" "External System"
# Relationships
u -> sws "Uses"
u -> sws.webShopFrontend "Accesses website via browser"
admin -> sws "Manages"
sws.webShopFrontend.productCatalog -> sws.webShopBackend.productService "Fetches product data from" "JSON/HTTPS"
sws.webShopFrontend.shoppingCart -> sws.webShopBackend.productService "Checks product availability" "JSON/HTTPS"
sws.webShopFrontend.checkout -> sws.webShopBackend.orderService "Creates orders via" "JSON/HTTPS"
sws.webShopFrontend.checkout -> sws.webShopBackend.paymentGateway "Processes payments via" "JSON/HTTPS"
sws.webShopFrontend.userAccount -> sws.webShopBackend.authService "Authenticates using" "JWT/HTTPS"
sws.webShopBackend.productService -> sws.db "Reads/writes product data to" "JPA/JDBC"
sws.webShopBackend.orderService -> sws.db "Stores orders in" "JPA/JDBC"
sws.webShopBackend.authService -> sws.db "Reads user credentials from" "JPA/JDBC"
sws.webShopBackend.paymentGateway -> paymentSystem "Processes payments using" "REST/HTTPS"
}
views {
# System Context View
systemContext sws "SystemContext" "Overview of the webshop system and its users" {
include *
autolayout lr
}
# Container View
container sws "Containers" "The containers that make up the webshop system" {
include *
autolayout lr
}
# Component Views
component sws.webShopFrontend "FrontendComponents" "Components within the webshop frontend" {
include *
autolayout tb
}
component sws.webShopBackend "BackendComponents" "Components within the webshop backend" {
include *
autolayout tb
}
styles {
element "Element" {
color white
}
element "Person" {
background #116611
shape person
}
element "Software System" {
background #2D882D
}
element "Container" {
background #55AA55
}
element "Component" {
background #77CC77
}
element "Code Element" {
background #99EE99
shape Box
}
element "Database" {
shape cylinder
}
element "External System" {
background #999999
}
}
}
}
Output
This code generates the following C4 diagrams. (You can double-click on the elements to zoom into containers and zoom out by “navigate back”.)
Visit in separate tab: C4 Model Example
(Generated by structurizr-cli )
Conclusion
The C4 model is a powerful tool for visualizing and documenting software architecture. By breaking down complex systems into manageable components, it helps teams understand and communicate their designs effectively. Whether you’re working on a small project or a large enterprise application, the C4 model can provide clarity and structure to your architecture discussions.
However, it should not be forgotten that the initial outlay is high but will be worthwhile.
